“Fear is not real. The only place that fear can exist is in our thoughts of the future.” — Will Smith
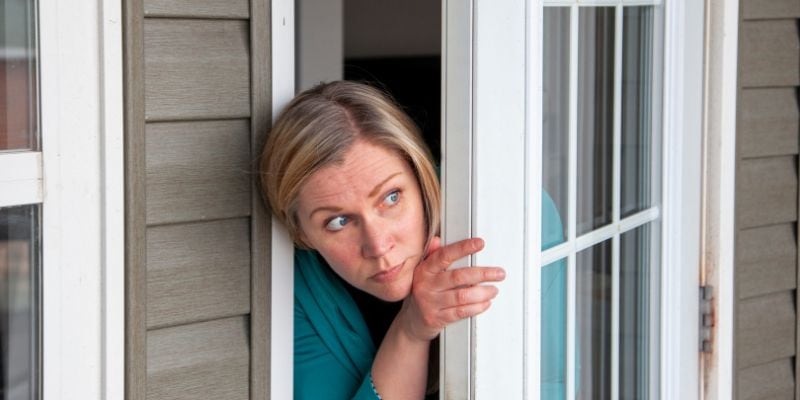
Struggling with the fear of leaving home or being in public spaces? Agoraphobia can make everyday life challenging, but help is available. This anxiety disorder can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making even routine activities feel overwhelming. However, individuals can regain confidence and freedom with the right support and treatment.
Agoraphobia often develops after experiencing intense anxiety or panic attacks. Over time, the fear of these episodes occurring in public or unfamiliar places leads to avoidance behaviours. Unfortunately, these avoidance patterns reinforce anxiety, making it even harder to break free from the cycle.
Common Symptoms of Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia manifests in both physical and emotional ways. Recognising these symptoms is the first step toward seeking help.
- Physical Symptoms:
-
- Increased heart rate and palpitations
- Shortness of breath or hyperventilation
- Dizziness or feeling lightheaded
- Nausea or stomach discomfort
- Sweating excessively
- Shakiness or trembling
- Chest tightness or discomfort
- Emotional and Psychological Symptoms:
-
- Fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult
- Avoidance of public places such as malls, theatres, or public transport
- Anxiety about being alone outside the home
- Feeling detached from reality or others
- Fear of embarrassment or losing control in public
- Constant worry about potential panic attacks
In severe cases, individuals with agoraphobia may become entirely housebound, affecting their personal relationships, work, and overall well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of agoraphobia isn’t fully understood, several contributing factors have been identified:
- History of Panic Attacks: Many individuals develop agoraphobia after experiencing intense panic attacks in certain situations.
- Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders can increase susceptibility.
- Trauma or Stressful Events: Sudden life changes, personal loss, or trauma can trigger agoraphobia.
- Personality Traits: Individuals prone to excessive worry or who have a heightened sensitivity to stress may be more at risk.
- Substance Use: Alcohol or drug abuse can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, including agoraphobia.
The Impact of Agoraphobia
The effects of agoraphobia extend beyond anxiety, affecting multiple aspects of life:
- Social Isolation: Avoidance of social situations can lead to loneliness and disconnection from loved ones.
- Career and Education Limitations: The inability to attend work or school regularly can create financial and professional setbacks.
- Health Issues: Chronic stress and anxiety can contribute to physical conditions like headaches, digestive issues, and fatigue.
Understanding these consequences highlights the importance of early intervention and treatment.
Treatment Options for Agoraphobia
Psychotherapy for Agoraphobia
Therapy is a fundamental approach to managing and overcoming agoraphobia. Different types of therapy address various aspects of the condition:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
- Helps individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns that fuel fear.
- Teaches coping strategies to manage anxiety in feared situations.
- Often includes exposure therapy, where individuals gradually face their fears in a controlled setting.
- Exposure Therapy:
-
- A structured approach that encourages step-by-step exposure to feared situations.
- It helps reduce avoidance behaviours over time.
- It can be done in person or using virtual reality for controlled exposure.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT):
- It focuses on accepting distressing thoughts rather than trying to eliminate them.
- Encourages mindfulness and staying present in the moment.
- It helps individuals commit to actions that align with their values despite anxiety.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR):
- Initially developed for trauma, EMDR therapy can help individuals process distressing memories related to their anxiety.
- Uses guided eye movements to reframe negative beliefs and reduce emotional distress.
- Hypnotherapy:
- Hypnotherapy uses deep relaxation techniques to help individuals access and reprogram fear-based responses.
- It can aid in reducing avoidance behaviours and increasing confidence in public spaces.
- Group Therapy and Support Groups:
- Provides a sense of community and support from others with similar experiences.
- Reduces feelings of isolation.
- Offers structured exposure exercises in a safe environment.
Medication for Agoraphobia (Prescribed by Doctors or Psychiatrists)
In some cases, medication may be prescribed alongside therapy to help manage symptoms. Common options include:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs):
Fluoxetine, Sertraline, or Paroxetine can help balance brain chemicals linked to anxiety.
- Benzodiazepines:
Used for short-term relief but should be taken with caution due to the risk of dependence (e.g., Alprazolam, Clonazepam).
- Beta-Blockers:
It can help manage the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and trembling.
Medication is not a standalone cure but can be an effective part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Self-Help Strategies to Overcome Agoraphobia
In addition to professional treatment, self-help techniques can support recovery:
- Gradual Exposure: Start by facing small, manageable situations before tackling larger fears.
- Breathing and Relaxation Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, and muscle relaxation can reduce anxiety levels.
- Journaling: Tracking thoughts and emotions can help identify patterns and triggers.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts mood and reduces stress.
- Social Support: Talking to trusted friends or family members provides emotional reinforcement.
- Limiting Stimulants: Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake can help prevent worsening anxiety symptoms.
Seeking Professional Help
If agoraphobia is affecting your daily life, professional help can provide structured support to help you:
- Regain confidence in public spaces.
- Reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Improve overall well-being and quality of life.
Insightful Counselling specialises in evidence-based treatments like CBT, exposure therapy, and hypnotherapy to help individuals overcome their fears.
Book a session today and take the first step towards reclaiming your freedom.
Conclusion
Agoraphobia can be overwhelming, but it is treatable. Whether through psychotherapy, counselling, medication, or self-help strategies, individuals can regain control over their lives and reduce anxiety.
By gradually facing fears and seeking support, those with agoraphobia can work towards leading independent, fulfilling lives. If you or someone you know is struggling, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance. Recovery is possible!
References:
-
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) – Anxiety Disorders: Agoraphobia
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders -
Cleveland Clinic – Agoraphobia: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15769-agoraphobia -
American Psychological Association (APA) – Exposure Therapy for Anxiety Disorders
https://www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/treatments/exposure-therapy -
Verywell Mind – What Is Agoraphobia?
https://www.verywellmind.com/agoraphobia-overview-4176851 -
National Health Service (NHS, UK) – Agoraphobia – Overview and Treatments
https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/conditions/agoraphobia/